
Silk is a natural fibre created by insects as they spin their cocoons. In the textile industry, it’s commonly sourced from silkworm cocoons, which are processed into yarn and then woven into fabric.
Known for its smooth texture, elegant sheen, and lasting durability, silk has been a prized material for centuries, often used in garments, upholstery, and bedding.
At Sealy, we incorporate silk fibre blends into the quilt layers of selected mattresses. We’ve chosen silk for its luxurious feel and strong, long-lasting quality. Discover more in our detailed guide.
What is silk?
Silk is a natural fibre known for its softness, lustre, and strength. It’s widely used in textiles for everything from clothing to bedding, thanks to its luxurious feel and durability.
Where does silk come from?
Silk is produced by insect larvae and arachnids, with the most common source being the caterpillars of the mulberry silkworm. These caterpillars spin silk to form their cocoons. While wild silkworms do exist, silk is typically sourced from domesticated silkworms raised specifically for this purpose–a practice known as sericulture.
It takes roughly 2000 to 3000 silkworms to produced just under half a kilogram of raw silk, making cultivation essential for large-scale production.
Silk cocoons and history
Silk farming began in ancient China, with archaeological evidence suggesting silk use as far back as 6,500 BC. Sericulture became more established during the Yangshao period (5,000-3,000 BC). Over time, the art of silk production spread to South Asia, India, the Mediterranean and parts of Europe.
Today, China remains the largest producer of silk, followed by India, Uzbekistan, and Vietnam.
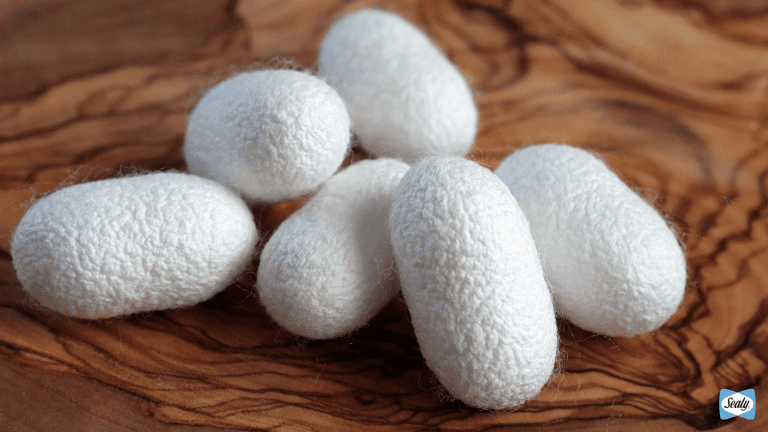

How is silk made?
The process begins with silkworms, which are fed a steady diet of mulberry leaves. After going through a moulting stage, the worms spin protective cocoons using silk threads.
To harvest the silk, the cocoons are placed in hot water or exposed to steam. This softens the natural gum that holds the cocoon together and ends the pupae stage. The fine silk filaments from several cocoons are then unwound and combined on a reel in a process called reeling.

These threads are then twisted together in a step known as throwing, which strengthens them into yarn suitable for dyeing, weaving, and commercial use.
While silk can still be handwoven, most large-scale production is done in factories or textile mills using specialised machinery to meet global demand efficiently.
What are the characteristics of silk fabric?
Silk has long been associated with elegance and comfort, but its appeal goes beyond just a smooth texture and luxurious sheen. Despite being incredibly lightweight, silk is remarkably strong– its fibres have a tensile strength that can surpass that of steel wire.
One of silk’s standout features is its excellent breathability and natural temperature regulation. It keeps you cool in hot weather and provides warmth in cooler conditions, making it a versatile fabric for all seasons.
Silk is also naturally hypoallergenic, making it gentle on sensitive skin and less likely to cause irritation compared to many synthetic or rougher materials.
Another practical benefit is its high absorbency. Silk can hold a good amount of moisture without feeling damp and dries quickly, making it ideal for daily wear and sleepwear. These qualities make silk not just a symbol of luxury, but also a smart and comfortable choice for everyday use.

What are the different types of silk?
Silk comes in various forms, each with unique characteristics depending on the insect species and the region it originates from. The most well-known and widely used is mulberry silk, produced by mulberry silkworms. This type is celebrated for its consistent high quality, smoothness, and natural sheen.
Beyond mulberry silk, other notable varieties include:
- Eri silk: Originating from India, eri silk is spun from eri silkworms. It has a coarser texture and a naturally darker tone. Known for its excellent insulation, it’s commonly used in warm clothing and soft furnishings.
- Muga silk: A rare and luxurious silk from Assam in northeast India, muga has a natural golden hue. It becomes shinier with age and retains its lustre even after repeated washing. Due to its beauty and durability, muga is often used in traditional attire and ceremonial garments.
- Tussar silk: Also golden in colour but rougher in texture, tussar is produced by a variety of wild silkworms across Asia. It is commonly used to make sarees and is prized for its unique texture and ability to hold vibrant dyes.
In addition to these types of raw silk, the way silk is woven can also affect the final fabric. For instance:
- Dupioni silk is made using uneven threads, creating a slightly rough, textured surface with natural slubs
- Charmeuse is woven to have a glossy, silky-smooth front and a dull matte back, ideal for garments like blouses and evening wear.
- Other common silk weaves include chiffon, crêpe, organza, and more– each offering different textures, drapes, and finishes suitable for a wide range of uses.
These varieties highlight silk’s versatility, from traditional wear to high-end fashion and home textiles.
What are the uses of silk?
Silk is an incredibly adaptable material, found in everything from fashion and beauty to home and even industrial applications.
Its natural sheen and fluid drape–especially in mulberry silk–make it a favourite for both women’s and men’s fashion. Though garments made from pure silk can be pricey, they are often seen as a symbol of elegance and refinement. You’ll find silk commonly used in accessories, sleepwear, designer apparel, and bridal gowns.
In the home, silk is a popular choice for luxurious furnishings such as curtains, pillowcases, bedsheets, and even upholstery for furniture. Thanks to its softness and elegant appearance, it adds a touch of sophistication to any interior.
Interestingly, silk also has practical uses beyond lifestyle and fashion. It has been used in items like parachutes, bicycle tires, surgical stitches, and even certain soaps– showing just how versatile and valuable this natural fibre truly is.
What are the pros and cons?
While silk is a luxurious and beautiful fabric, there are some disadvantages to consider.
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| Strong | Expensive |
| Hypoallergenic | Delicate laundering |
| Moisture-wicking | May fade in sunlight |
| Temperature regulating | Prone to water stains |
| Soft and smooth texture |
Is Silk Sustainable?
Silk is more sustainable than many synthetic fabrics because it’s natural, renewable, and biodegradable. This means it breaks down over time without harming the environment.
What are the alternatives?
There are some fabric alternatives that replicate the softness and sheen of silk. These include satin, rayon, viscose, cupro, and bamboo lyocell, which is a similar material to Tencel. There are also some vegan silks made of bananas, pineapples, lotus and cactus.
Sealy and Silk
At Sealy, we incorporate silk into the quilt layers of select mattress models. We choose silk blends for their natural strength, durability, and smooth, luxurious feel–qualities that enhance overall comfort and sleep quality.
If you’re interested in a Sealy mattress that features silk, feel free to reach out to our team for guidance on the best option for your needs.

Silk FAQ
Silk is an animal-based product, made by silkworms which are usually killed during the production process. Because of this, many vegans choose to avoid silk and opt for plant-based or synthetic alternatives instead.
Peace silk, or Ahimsa silk, is made in a way that allows silkworms to complete their life cycle and emerge naturally from their cocoons, avoiding harm to the insects. Because the process is more labour-intensive and produces less usable fibre, this type of silk tends to be significantly more expensive than conventional silk.
Silk is known to feel softer than cotton, with better moisture wicking properties and temperature regulation. It is also more hypoallergenic than cotton.
Pure silk is natural, derived from silkworms. Silk may be dyed or blended with synthetic fibres. The fabric label should specify whether any synthetic blends have been used.
Silk should be hand-washed with delicate detergent in cold water. Hang or lay flat to dry, avoiding direct sunlight. Keep away sharp objects such as jewellery that may cause the material to be damaged.





